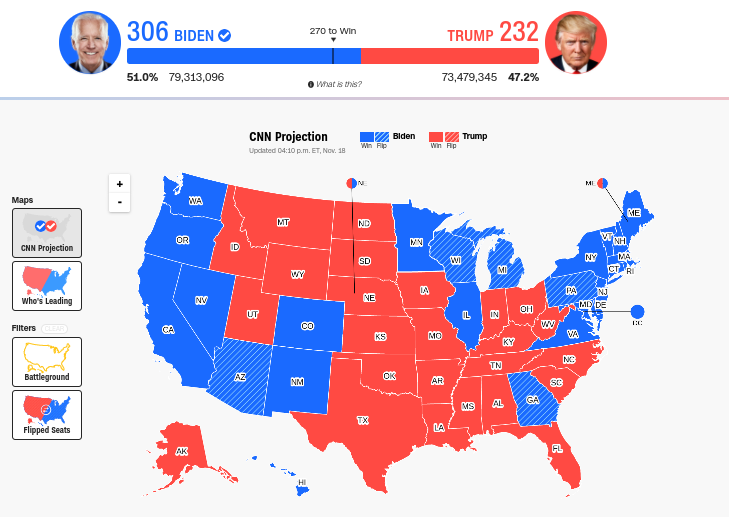
The 2020 electoral college map played a pivotal role in shaping the outcome of one of the most significant presidential elections in recent U.S. history. As the nation grappled with unprecedented challenges, the electoral college system became a focal point of discussion and debate. Understanding how this system works is crucial for anyone interested in American politics and governance.
The 2020 election was marked by record voter turnout, widespread use of mail-in ballots, and intense scrutiny over electoral processes. The electoral college map not only determined the winner but also highlighted the importance of battleground states in deciding the presidency. This article delves deep into the intricacies of the 2020 electoral college map, offering valuable insights into its workings and implications.
By exploring the historical context, key players, and critical factors that influenced the 2020 electoral college map, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of how the U.S. presidential election system operates. Whether you're a political enthusiast or simply curious about democracy, this guide will provide clarity and depth on this vital topic.
Read also:Gary Cooper The Legendary Actor Who Redefined Hollywood Stardom
Table of Contents
- Introduction to the Electoral College
- History of the Electoral College
- 2020 Electoral College Results
- Key Swing States in 2020
- Impact of Battleground States
- Electoral Vote Distribution
- Challenges Faced in 2020
- Potential Reforms to the Electoral College
- Data and Statistics
- Future Implications of the Electoral College
Introduction to the Electoral College
The electoral college is a unique system used in the United States to elect the president and vice president. Established by the Founding Fathers as a compromise between election by Congress and direct popular vote, it allocates electoral votes based on the number of representatives each state has in Congress. This system ensures that smaller states have a proportionate voice in the election process.
How the Electoral College Works
In the 2020 election, the electoral college map was closely watched as each state's electoral votes determined the ultimate winner. A candidate needs at least 270 electoral votes out of 538 total to secure victory. The map highlights how states with higher populations, like California and Texas, carry more weight, while smaller states like Wyoming and Vermont have fewer electoral votes.
History of the Electoral College
The origins of the electoral college date back to the Constitutional Convention of 1787. Designed to balance power between large and small states, the system has evolved over time. While it has faced criticism, it remains a cornerstone of American democracy.
Key Historical Developments
- 1800 Election: The first major controversy when Thomas Jefferson and Aaron Burr tied in electoral votes.
- 1824 Election: Andrew Jackson won the popular vote but lost the presidency due to the electoral college.
- 2000 Election: George W. Bush won despite losing the popular vote to Al Gore.
2020 Electoral College Results
The 2020 electoral college map revealed a clear victory for Joe Biden, who secured 306 electoral votes compared to Donald Trump's 232. Key states like Pennsylvania, Michigan, and Arizona played decisive roles in tipping the balance.
State-by-State Breakdown
Below is a summary of how states contributed to the final tally:
- California: 55 electoral votes for Biden.
- Texas: 38 electoral votes for Trump.
- Pennsylvania: 20 electoral votes for Biden.
Key Swing States in 2020
Swing states, also known as battleground states, are crucial in determining the outcome of any presidential election. In 2020, states like Wisconsin, Michigan, and Arizona were closely contested and ultimately decided the election.
Read also:Aaron Eckhart A Journey Through Hollywoods Most Versatile Actor
Why Swing States Matter
Swing states often have a mix of urban, suburban, and rural voters, making them highly competitive. Campaigns focus heavily on these states, investing resources and time to sway undecided voters.
Impact of Battleground States
The influence of battleground states on the 2020 electoral college map cannot be overstated. These states often reflect broader national trends and can shift political power significantly.
Factors Influencing Swing States
- Economic conditions.
- Demographic changes.
- Voter turnout initiatives.
Electoral Vote Distribution
The distribution of electoral votes across states is based on population, as determined by the census. Larger states naturally carry more weight, but smaller states still hold significant sway due to the minimum number of electoral votes allocated to each.
Understanding Proportional Representation
While most states follow a winner-takes-all approach, Nebraska and Maine use a proportional system, awarding electoral votes based on congressional district results. This adds complexity to the electoral college map.
Challenges Faced in 2020
The 2020 election posed numerous challenges, from the COVID-19 pandemic to misinformation campaigns. Ensuring the integrity of the electoral process was a top priority for election officials nationwide.
Addressing Misinformation
Efforts to combat misinformation included collaboration between social media platforms, election authorities, and independent fact-checkers. Transparency and communication were key to maintaining public trust.
Potential Reforms to the Electoral College
Debates over reforming the electoral college have intensified in recent years. Proposals range from adopting a national popular vote to restructuring the allocation of electoral votes.
Arguments for and Against Reform
- Supporters argue that reform would make every vote count equally.
- Opponents contend that the current system protects smaller states' interests.
Data and Statistics
Data from the 2020 election provides valuable insights into voter behavior and trends. According to the U.S. Election Assistance Commission, over 159 million Americans cast their ballots, a record turnout.
Key Statistics
- Turnout rate: Approximately 66.8% of eligible voters participated.
- Mail-in ballots: Over 100 million votes were cast by mail due to the pandemic.
Future Implications of the Electoral College
The 2020 electoral college map serves as a blueprint for understanding future elections. As demographic shifts and technological advancements continue to reshape the political landscape, the role of the electoral college will remain central to American democracy.
Preparing for Future Elections
Election officials and policymakers must prioritize modernizing voting systems, enhancing cybersecurity, and ensuring equitable access to the ballot box. These steps are essential for maintaining the integrity of the electoral process.
Conclusion
The 2020 electoral college map highlighted the complexities and nuances of the U.S. presidential election system. By examining the historical context, key states, and challenges faced during the election, we gain a deeper appreciation for the importance of this institution. As we look toward the future, it is crucial to address potential reforms and ensure that every voice is heard in the democratic process.
We invite you to share your thoughts and insights in the comments section below. For more in-depth analysis of American politics, explore our other articles and resources. Together, we can foster a better understanding of the electoral college and its impact on our nation's future.