Infiltration and extravasation are two critical medical conditions that healthcare providers must understand thoroughly to ensure patient safety and optimal outcomes. These terms refer to the unintentional administration of fluids or medications outside the intended vascular pathway, which can lead to severe complications if not managed properly. As such, it is essential for medical professionals and patients alike to recognize the differences between these conditions and learn how to prevent and address them.
In the world of modern medicine, the administration of intravenous (IV) fluids and medications is a common practice. However, with the increasing complexity of treatments, the risks associated with infiltration and extravasation have become more pronounced. Understanding these risks and how to mitigate them is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients.
This article aims to provide a detailed overview of infiltration vs extravasation, including their definitions, causes, symptoms, prevention strategies, and management techniques. By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of these conditions and how they impact patient care.
Read also:Danny Lloyd The Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry
Table of Contents
- Definition of Infiltration and Extravasation
- Causes of Infiltration vs Extravasation
- Symptoms of Infiltration and Extravasation
- Diagnosis and Assessment
- Management Strategies
- Prevention Techniques
- Potential Complications
- Treatment Options
- Rehabilitation and Follow-Up
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Definition of Infiltration and Extravasation
Infiltration and extravasation are terms used in medical practice to describe the accidental leakage of infused substances from the vascular system into surrounding tissues. While both conditions involve fluid leakage, they differ based on the type of substance involved.
Infiltration
Infiltration occurs when non-vesicant solutions or fluids inadvertently leak into the surrounding tissues. This condition is typically less severe than extravasation but can still cause significant discomfort and complications if not addressed promptly.
Extravasation
Extravasation, on the other hand, involves the leakage of vesicant substances, which are more toxic and can cause severe tissue damage. Vesicants include certain chemotherapy drugs, irritant solutions, and other potent medications. Immediate intervention is critical to minimize tissue injury.
Causes of Infiltration vs Extravasation
Understanding the causes of infiltration and extravasation is essential for preventing these conditions. Below are some of the primary factors that contribute to these complications:
- Improper catheter placement or insertion technique
- Dislodgement or movement of the catheter
- Small or fragile veins, particularly in pediatric or elderly patients
- High infusion rates or pressure
- Patient movement or lack of immobilization
By addressing these risk factors, healthcare providers can significantly reduce the incidence of infiltration and extravasation.
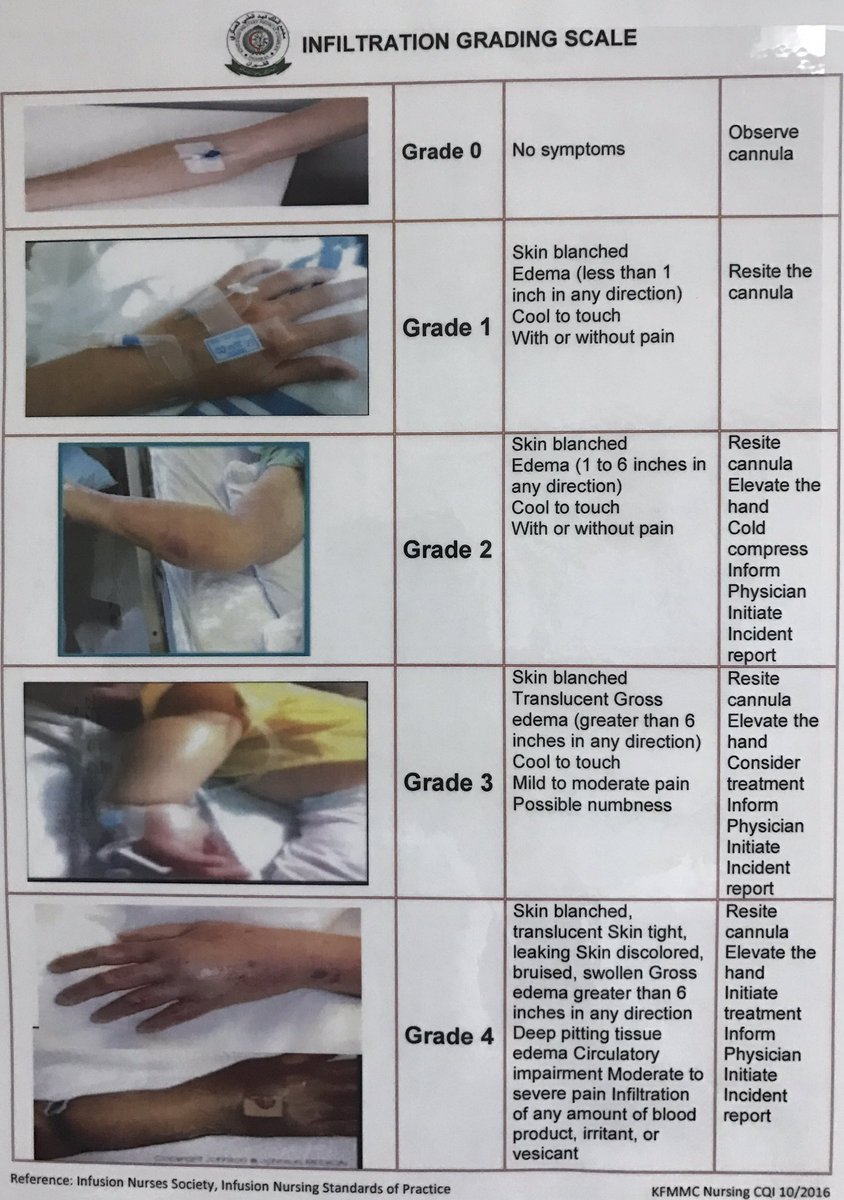
Symptoms of Infiltration and Extravasation
Recognizing the symptoms of infiltration and extravasation is crucial for early detection and intervention. Below are the common signs associated with each condition:
Read also:Jane Hajduk A Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry
Symptoms of Infiltration
- Swelling at the infusion site
- Coolness or pallor of the affected area
- Pain or discomfort
- Slowed or stopped infusion
Symptoms of Extravasation
- Burning or stinging sensation
- Redness or warmth at the site
- Blistering or skin discoloration
- Severe pain or tissue necrosis
It is important to note that symptoms may vary depending on the type of substance involved and the severity of the condition.
Diagnosis and Assessment
Accurate diagnosis and assessment are critical for effective management of infiltration and extravasation. Healthcare providers should:
- Conduct a thorough physical examination of the affected area
- Review the patient's medical history and current treatment plan
- Assess the type of infused substance and its potential effects
- Monitor for changes in symptoms over time
In some cases, imaging studies or other diagnostic tools may be necessary to evaluate the extent of tissue damage.
Management Strategies
The management of infiltration and extravasation depends on the severity of the condition and the type of substance involved. Below are some general strategies for managing these complications:
Infiltration Management
- Stop the infusion immediately
- Elevate the affected limb to reduce swelling
- Apply warm or cold compresses as appropriate
- Monitor the site for signs of improvement or worsening
Extravasation Management
- Follow institutional protocols for vesicant exposure
- Administer antidotes or counteragents as prescribed
- Consider advanced interventions such as surgical debridement
- Provide pain management and supportive care
Timely intervention is key to minimizing tissue damage and promoting recovery.
Prevention Techniques
Preventing infiltration and extravasation requires a proactive approach from healthcare providers. Some effective prevention strategies include:
- Proper catheter placement and securement
- Regular monitoring of infusion sites
- Using appropriate devices and techniques for high-risk infusions
- Educating patients and caregivers about signs to watch for
Implementing these measures can help reduce the risk of complications and improve patient outcomes.
Potential Complications
Both infiltration and extravasation can lead to serious complications if not managed appropriately. Some potential complications include:
- Tissue necrosis or ulceration
- Infection at the affected site
- Scarring or disfigurement
- Chronic pain or reduced mobility
Preventing these complications requires prompt recognition and treatment of infiltration and extravasation.
Treatment Options
Treatment for infiltration and extravasation varies depending on the severity of the condition and the type of substance involved. Below are some common treatment options:
- Topical creams or ointments to reduce inflammation
- Oral or intravenous medications for pain management
- Surgical intervention for severe tissue damage
- Physical therapy to restore function and mobility
Healthcare providers should tailor treatment plans to meet the specific needs of each patient.
Rehabilitation and Follow-Up
Rehabilitation and follow-up care are essential components of managing infiltration and extravasation. Patients may require:
- Ongoing monitoring of the affected site
- Physical therapy to restore strength and mobility
- Regular follow-up appointments to assess progress
By providing comprehensive follow-up care, healthcare providers can help patients achieve optimal recovery and minimize the risk of long-term complications.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Infiltration and extravasation are critical medical conditions that require prompt recognition and intervention. By understanding the differences between these conditions, their causes, symptoms, and management strategies, healthcare providers can improve patient safety and outcomes. Patients and caregivers also play an important role in recognizing signs of these complications and seeking timely care.
We encourage readers to share this article with others who may benefit from this information. Additionally, feel free to leave comments or questions below, and don't hesitate to explore other informative articles on our site. Together, we can promote safer and more effective healthcare practices for everyone.
For further reading, consider consulting reputable sources such as the National Center for Biotechnology Information and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for the latest research and guidelines on infiltration and extravasation.